 THE BIG PICTURE
THE BIG PICTURE
Black Box VR’s science-backed workout is a serious resistance training + HIIT cardio workout program. It gives you an intense full-body strength training workout in only 30 minutes! It breaks down like this:
- You’ll complete 14 – 18 sets of resistance exercises per 30-minute workout. The time flies by when you are having fun!
- These full-body workouts should be done 3 – 4 times per week help you hit science-based exercise volume goals for fast results.
- Your workout will be focused around compound exercises for time efficiency. No more wasted effort!
- You’ll do 12 – 14 reps per set at 60 – 70% of your automatically calculated one rep max weight. Push hard to force your body to change.
- The resistance is provided by our electronically-controlled cable pulley machine that moves by itself to the correct exercise position based on your height. It’s like a weight machine at your gym, but you don’t have to set it up!
- Cardio, agility, and speed exercises are integrated between resistance exercise sets. It’s a true athletic sport that anyone can learn.
The best part? You don’t have to do anything except play the game, and we’ll handle the rest. Black Box VR is your personal trainer, support system, and motivational coach.
Wouldn’t it be great if you could play an exciting video game and level up your own body instead of just your on-screen characters? That’s the revolutionary promise of Black Box VR.
Of course, if our workout program doesn’t give you real-life fitness results, you might as well stay on the couch and just play another 100 hours of Call of Duty. Why go to our virtual sport training center if it’s not going to be really, really effective? That would be a huge waste of time.
We know that the most important thing about Black Box VR is our ability to help you transform your body, health, and life. Nothing else matters and everything else is just tactics. That’s why we start every major company meeting with our mission statement:
“At Black Box VR, we help our members transform their lives through addictive fitness experiences that harness the power of immersive technologies.”
The founders of Black Box VR, Ryan DeLuca, and Preston Lewis, have 33 years of combined fitness industry experience. By founding and running the largest and most-visited fitness website in the world, Bodybuilding.com, they worked directly with millions of real people and helped create an uncountable number of awe-inspiring physical transformations.
Their love of innovative new technology combined with their expertise in exercise, sports psychology, nutrition, and supplements helped them to create content, products, and software that made the difference for loyal Bodybuilding.com visitors and customers. (And helped the company grow to nearly $500,000,000 in annual revenue.)
So it’s no surprise that when they started Black Box VR, the very first goal was to make sure that the workout experience was based on effective and efficient exercise science. We’re not talking about outdated “bro-science” either. We’re using data from exciting new studies, hot off the press. It’s not just our use of virtual reality which is state-of-the-art, it’s the use of the new science of physical transformation.
But you don’t have to worry about all of that. You just play our addictive game and let us handle the rest. (You can also focus on your new wardrobe and acting humble when people tell you how great you look.)
If you do want to learn more about the exercise programming and science behind Black Box VR, put your lab coat on, grab your clipboard, and read on.
What Is The Black Box VR Workout?
First, here is a simple explanation of our workout program.
It’s a resistance training + HIIT workout program. It’s structured like this:
- 14 – 18 sets of resistance exercises per 30-minute workout
- Full-body workouts, 3x – 4x per week to hit body part volume goals
- Focused on compound exercises for time efficiency
- 12 – 14 reps per set to (or just shy of) momentary muscular failure at 60 – 70% of one rep max weight
- Resistance is provided by our electronically-controlled cable pulley machine that moves by itself to the correct exercise position based on your height
As an example, this is a workout log from a typical battle from one of our members:
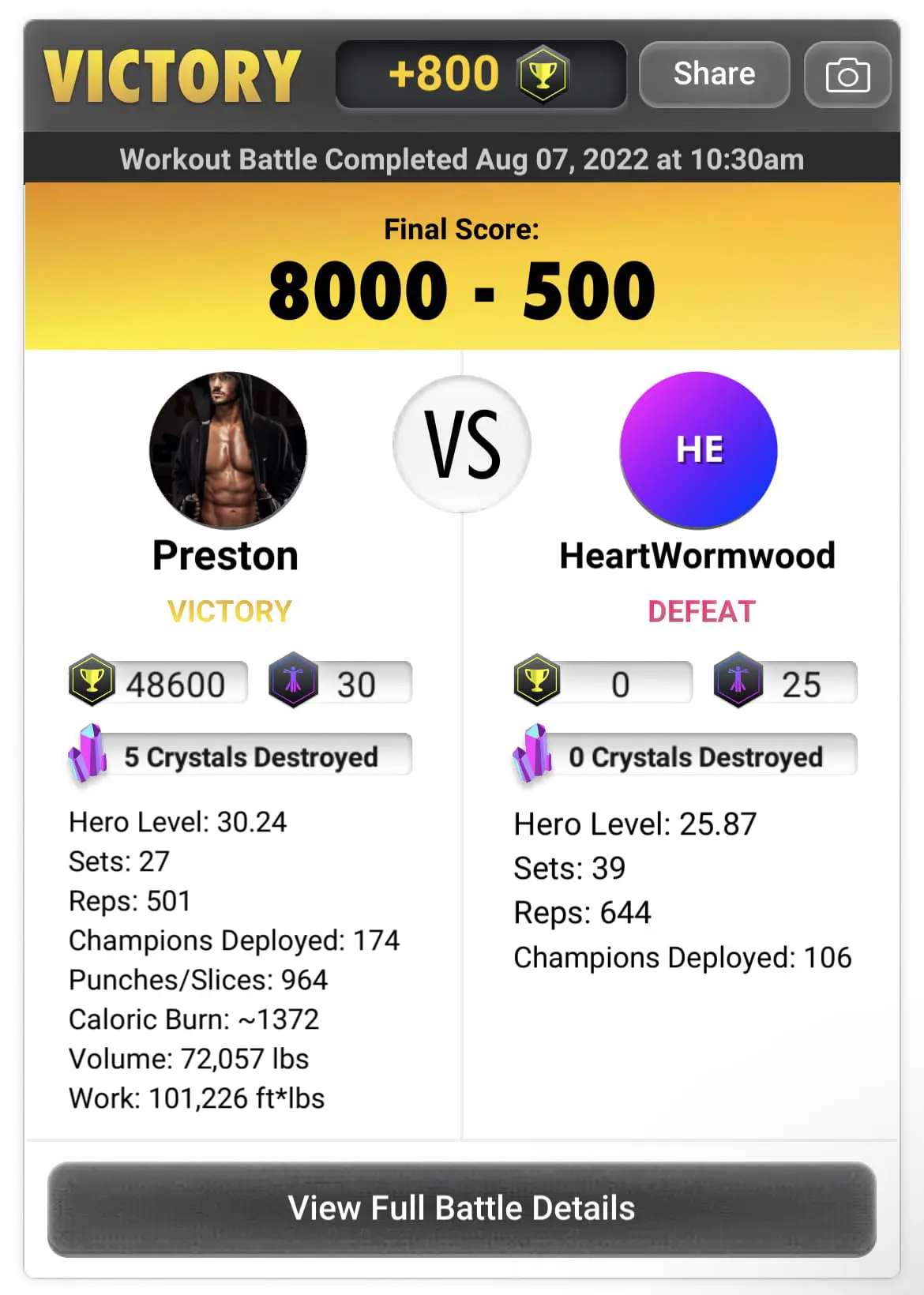
This shows that the member completed 27 compound exercise sets and 501 repetitions and did 72,057 pounds of volume. Volume is calculated as “weight x reps” for every set. Also, this member did 101,226 ft x lbs. of Work. Work takes into account sets, reps and also the cable displacement so Work numbers should always be higher than Volume numbers or it might indicate a user is doing shorter reps than they should be doing.
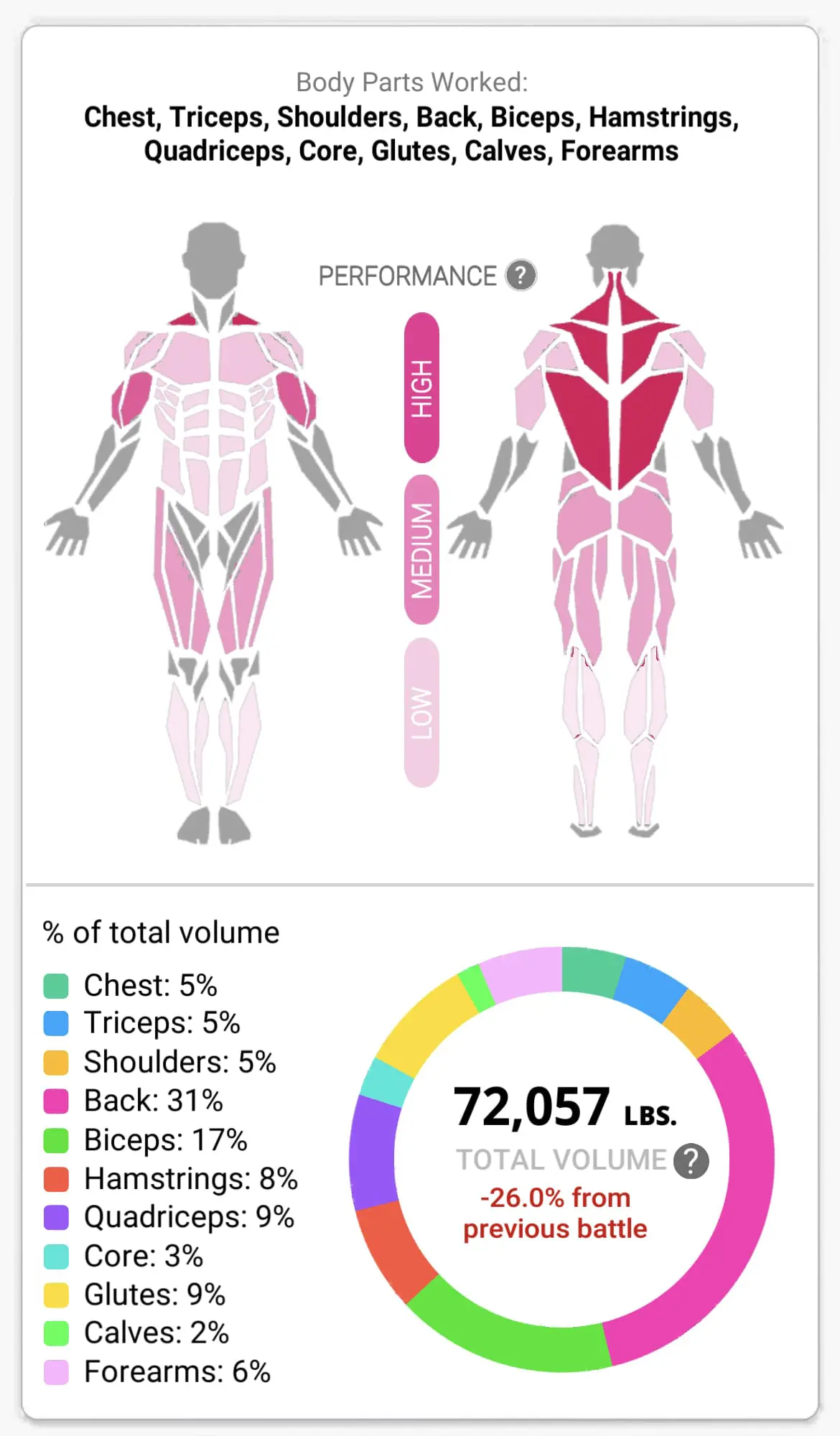
Their body part volume breakdown for this workout is shown in the app:
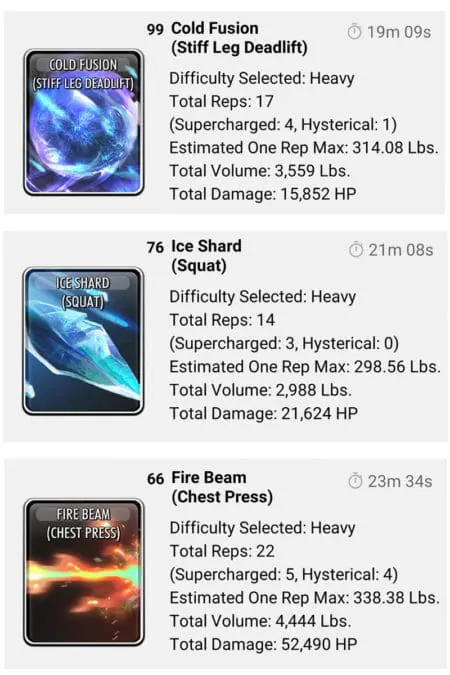
Every set is monitored and saved in the cloud database. You can see your individual set performance in the battle log. Some examples from this member:
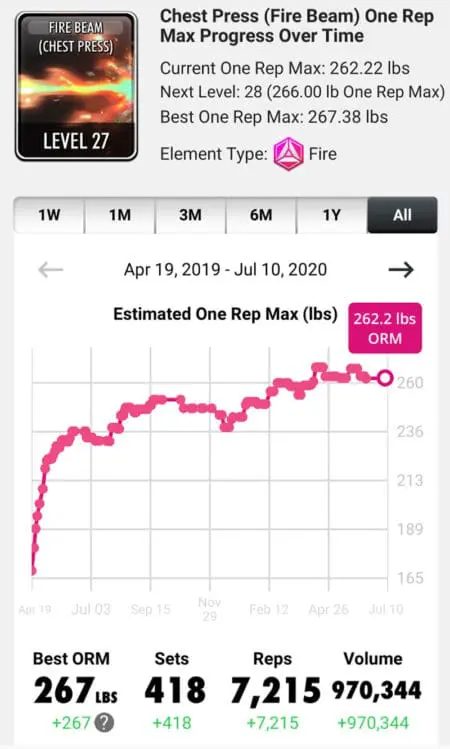
We also track your one-rep max performance by exercise and show it in the app:
Why Did We Choose These Workout Principles and Parameters?
Let’s break it down and get all science-y.
1. Resistance training is more effective than cardio-only
It turns out that just doing aerobics won’t help you get the body that you are craving. Cardio activities like running, spinning, and Zumba are good for building your cardiovascular endurance, strengthening your heart and lungs, and burning extra calories. Unfortunately, without resistance training, you’ll have a hard time getting the shape, strength, and leanness that you want.
Putting resistance training together with high-intensity cardio burns more calories in less time than cardio alone. After a spin bike session, your body stops burning extra calories right after you step off the bike. But with resistance training? Your body’s metabolism stays higher for up to 24 hours, burning extra calories while you are resting, and even while you are sleeping.

Resistance training is the most effective way to build strength, shape your arms, build your butt, earn that elusive six-pack, and get the swimsuit-ready body that gets attention. Nobody wants a skinny-fat body.
Oh, and resistance training also helps with:
- Reducing anxiety
- Reducing depression
- Improving sleep and reducing insomnia
- Improving bone health
- Building stronger joints
- Improving flexibility and balance
- Improving posture
- Preventing or the controlling of chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, arthritis, back pain, and obesity
- Reducing the risk of osteoporosis
- Improving your sense of well-being and body image
- Increasing self-esteem
- Enhancing your performance of everyday tasks
Just do it. We’ll make it easy and fun for you.
STUDIES
A mathematical model of the effects of resistance exercise-induced muscle hypertrophy on body composition
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29256047/
Effect of acute resistance exercise on postexercise energy expenditure and resting metabolic rate
https://journals.physiology.org/doi/abs/10.1152/jappl.1993.75.4.1847
EPOC Comparison Between Isocaloric Bouts of Steady-State Aerobic, Intermittent Aerobic, and Resistance Training
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/02701367.2014.999190?journalCode=urqe20
Effect of an acute period of resistance exercise on excess post-exercise oxygen consumption: implications for body mass management
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00421-001-0568-y?LI=true
Resistance Training Is an Effective Tool against Metabolic and Frailty Syndromes
https://www.hindawi.com/journals/apm/2011/984683/
Resistance Training is Medicine: Effects of Strength Training on Health
Comparative effectiveness of aerobic, resistance, and combined training on cardiovascular disease risk factors: A randomized controlled trial
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0210292
The Effects of Resistance Exercise Training on Anxiety: A Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs40279-017-0769-0
Twice-weekly progressive resistance training decreases abdominal fat and improves insulin sensitivity in older men with type 2 diabetes
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15735205/
Strength training improves muscle quality and insulin sensitivity in Hispanic older adults with type 2 diabetes
2. Weekly workout volume is the key factor in muscle building
Recent studies over the last decade have uncovered the key to building muscle: weekly volume. There is a dose-response relationship between the amount of volume you do per body part per week and your muscle gains. Up to a certain point, the more the better.
Volume is defined as:
Weight x Reps x Sets
For example, if you do 12 bench press reps with 100 pounds, you did 1200 pounds of volume for that set (12 x 100).
To get your total volume for your workout, add up all of the volume from each set. For example:
Bench Press
12 x 100 lbs. = 1200 pounds of volume
12 x 90 lbs. = 1080 pounds of volume
15 x 50 lbs. = 750 pounds of volume
Total volume for all sets: 3030 pounds
To build muscle, there is a minimum amount of volume that you need to do per week. Obviously, you aren’t going to stress the body enough with one set of bench press per week. There is a lower limit that has to be passed for you to see results.
On the flip side, there is also a maximum amount of volume you can do without leading to overtraining and overstressing your body. Beyond a certain threshold, you actually reduce your results and can start to get injuries and other negative health effects.
So what’s the sweet spot?
Let’s talk about one of the most recent studies done on the dose-response relationship between total volume and strength/muscle gains.
The researchers studied three groups. Each group did a full-body workout consisting of seven exercises, three times per week for eight weeks. One group did one set per exercise, three times per week. The second group did three sets per exercise and the third group did five sets. They measured muscular endurance, strength, and muscle thickness at the beginning and end of the study.

All groups improved their strength and endurance and there was not a significant difference between groups. It seems that strength gains are similar whether you are doing one set, three sets, or five sets of each exercise, three times a week.
They found that doing more sets (up to five) gave slightly more gains in hypertrophy compared to less sets. It was clear that doing one set was not as effective as doing three or five. The evidence found a very slight benefit to doing five sets compared to three.
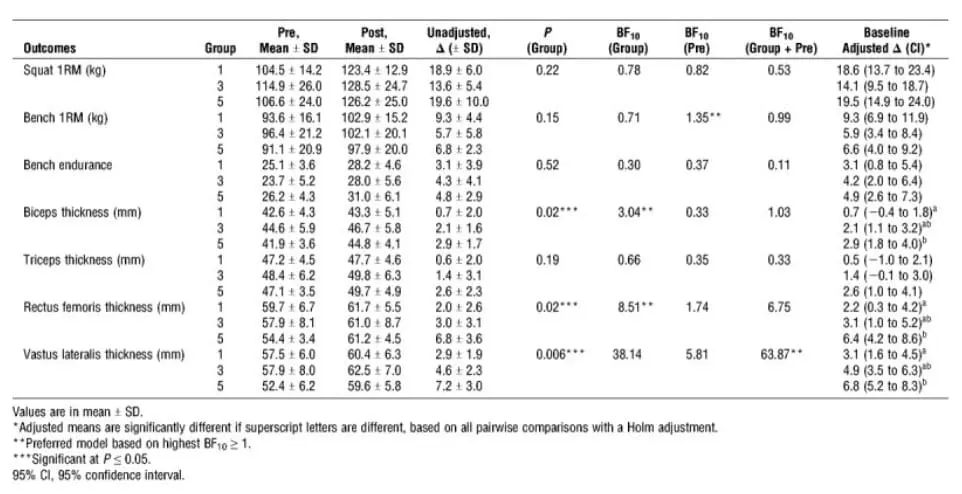
At Black Box VR, we tuned our weekly volume to be similar to the group that did three sets per exercise, three times per week. Why? The difference in benefits between three and five was small, but the time you save by doing less sets helps our members to stick to their programs. A shorter workout that gives you most or all of the results of a longer one is preferred because it’s easier to adhere to. If you have a two-hour workout tomorrow morning, it’s easy to find excuses to miss it. A quick 30-minute workout? That’s no problem. And as we all know, consistency is the only real secret of fitness success.
We also focus on compound exercises like cable squats and standing rows. These exercises target multiple muscle groups at once, saving you time and giving you functional fitness results. Too many “bros” and “fitness gals” spend too much time doing unnecessary isolation exercises that don’t translate to real-world results.
STUDIES
A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Resistance Training on Whole-Body Muscle Growth in Healthy Adult Males
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32079265/
Effects of different volume-equated resistance training loading strategies on muscular adaptations in well-trained men
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24714538/
Volume-equated high- and low-repetition daily undulating programming strategies produce similar hypertrophy and strength adaptations
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27218448/
Resistance Training Volume Enhances Muscle Hypertrophy but Not Strength in Trained Men
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6303131/
Dose-Response Relationship of Weekly Resistance-Training Volume and Frequency on Muscular Adaptations in Trained Men
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30160627/
Dose-Response Relationships of Resistance Training in Healthy Old Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26420238/
Single vs. multiple sets of resistance exercise for muscle hypertrophy: a meta-analysis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20300012/
The Minimum Effective Training Dose Required to Increase 1RM Strength in Resistance-Trained Men: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
3. Pushing yourself close to muscular failure on most sets is necessary for strength and muscle gains
Research has shown that to maximize your results from your resistance training, you must push yourself in almost every set. A recent meta-analysis found that training just shy of momentary muscular failure (where you can’t do another rep) gives you the best strength and muscle gains. You don’t need to go to full failure, but you need to be close, likely within one to two reps.
Going to failure on every set increases your recovery time, making it so that you get fewer reps during subsequent sets. As we know, volume is the main driver for muscle growth, so doing fewer reps or reducing your resistance will decrease your overall volume. Studies also show that your strength could remain lower up to 48 – 72 hours after going to full failure, so even your next workout could suffer.

Of course, the real problem is that most people don’t even push themselves close to this hard. They choose a dumbbell weight for chest press that they could do 20 reps with but only do 12. They stop short of pushing themselves to the uncomfortable zone and end up sabotaging their workout results.
The Black Box VR experience uses serious gamification, competition, and rewards to motivate you to give it your all. Studies on virtual reality show that pain perception decreases while in VR, so you’ll feel comfortable doing more reps without fully feeling the burn. That means more volume and a more pleasant workout experience.
STUDIES
Effect of Training Leading to Repetition Failure on Muscular Strength: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26666744/
Effect of Resistance Training to Muscle Failure vs. Volitional Interruption at High- and Low-Intensities on Muscle Mass and Strength
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29189407/
Is repetition failure critical for the development of muscle hypertrophy and strength?
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25809472/
Time Course of Recovery From Resistance Exercise With Different Set Configurations
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30036284/
Skeletal Muscle Fiber Adaptations Following Resistance Training Using Repetition Maximums or Relative Intensity
4. You have to increase the amount of work you do over time for your body to keep changing
You see it every day at your local Globo-gym: people grinding away at the elliptical while watching their favorite Netflix show or people doing set after set of bicep curls with the same weight they always use.
What don’t you see? Any difference in their bodies over months or even years. What a waste of time!
To get leaner, stronger, and more fit you have to push your body beyond what it can do today. A good personal trainer records what their clients do in detail, and changes the workout constantly to make sure they never plateau.
Black Box is an AI personal trainer that’s tracking what you are doing on our virtual clipboard. If your real-life trainer sees that you got 25 reps with a given weight, but she wanted you to be able to get only 15 reps, she increases the weight by a decent amount. She then sees that you got 16 reps when she wanted you to get 15 reps so she increases the weight by a small amount. Then she sees you got 12 reps when she wanted you to get 15, so she decreases the weight slightly. (We also consider other factors like exhaustion, incomplete sets, rolling averages over multiple workouts, and more.)

This is the powerful principle known as Progressive Overload. If you don’t increase your resistance, reps, and/or total workout volume over time, your body will not be forced to change and you will plateau. The key is to progress at the right rate. If you move up your weights too fast, you could sacrifice your exercise form and get an injury.
Our AI personal trainer monitors your form, provides exercise instruction and videos, and tells you when you are doing it wrong (e.g. the exercise attack doesn’t fire).
All you have to do is play the game. We track everything for you and give you detailed stats and charts in the Black Box VR companion app.
STUDIES
Fundamentals of Resistance Training: Progression and Exercise Prescription
American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Progression models in resistance training for healthy adults
5. Choosing the right resistance levels and intensity makes a difference
It used to be “common gym knowledge” that if you want to gain strength, you do 3 – 5 reps per set. If you want to gain muscle, do 8 – 12 reps per set. Muscular endurance? 15 – 20 reps per set.
Once again, new studies show that your chosen rep range is not as important as it was previously thought.
Newer studies are showing that hypertrophy gains are similar from intensities between 30 – 80% of one-rep max. It’s been kind of surprising to us actually, but that’s what they have proven. You can make the same hypertrophy gains (and great strength gains) by using pretty light weights and 25 – 35 reps per set, you just have to be sure to match the volume of somebody doing 8 – 12 reps.

We chose to set the intensity at a level where people can get 12 – 14 reps per set (before muscular failure) which seems to be the good middle ground for time efficiency, strength gains, and hypertrophy.
When you first start at Black Box VR, the resistance will be set very low for you to learn the exercises and learn how to play the game. We monitor each set and if you can do more, we raise the resistance. The goal is to get you to that 12 – 14 rep range per set and then help you get stronger from there.
The fun part? The more resistance you can handle, the more damage you will do to your competitor with each rep. You’ll be moving up the Arena levels in record time.
STUDIES
Effects of Low- vs. High-Load Resistance Training on Muscle Strength and Hypertrophy in Well-Trained Men
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25853914/
Is there a minimum intensity threshold for resistance training-induced hypertrophic adaptations?
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23955603/
Effects of 4, 8, and 12 Repetition Maximum Resistance Training Protocols on Muscle Volume and Strength
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32304514/
Total Number of Sets as a Training Volume Quantification Method for Muscle Hypertrophy: A Systematic Review
6. Full-body workouts are as effective or more effective than split body-part routines
This is another classic gym myth that won’t go away.
Ask most lifters in the gym about their workout program, and it will likely be a “bro split” where they do chest and triceps on Monday, back and biceps on Tuesday, and so on (with Friday leg day getting skipped most of the time).
As we learned, the most important factor for results is the amount of volume per week per body-part that you are getting. It doesn’t matter if you do all of the volume over a few days or over many days per week. The dose of volume is the key.

It turns out that you can get more volume, in less time, by working each body part multiple times per week. Instead of doing chest exercises on Monday and then not doing more until the next Monday, you can get more volume by doing chest exercises three times a week.
Why? Here’s one reason.
If you try to do nine sets of chest exercises in one day, your latter sets will be lower volume. By the end of your workout, your chest is exhausted and can’t lift as much as when it was freshly rested. For example, your workout may looks like this:
Set 1: 200 x 12 = 2400 lbs.
Set 2: 200 x 10 = 2000 lbs.
Set 3: 200 x 8 = 1600 lbs.
Set 4: 175 x 8 = 1400 lbs.
Set 5: 160 x 8 = 1280 lbs.
Set 6: 160 x 8 = 1280 lbs.
Set 7: 135 x 10 = 1350 lbs.
Set 8: 135 x 9 = 1215 lbs.
Set 9: 135 x 8 = 1080 lbs.
Total weekly chest volume: 13,605 lbs.
By the time you hit your last set, your chest is burning and can’t even do half the volume as you could your first set. The only way around this is to have really long rest times between your sets (which is actually recommended by studies since it gives you more volume per workout). But even then, your chest and other muscles will be tired and unable to do what you can do when you are fully recovered.
Instead, you can work your chest three times per week and split the sets up between each workout:
Day One
Set 1: 200 x 12 = 2400 lbs.
Set 2: 200 x 10 = 2000 lbs.
Set 3: 200 x 8 = 1600 lbs.
Total chest volume: 6000 lbs.
Day Two
Set 1: 200 x 12 = 2400 lbs.
Set 2: 200 x 10 = 2000 lbs.
Set 3: 200 x 8 = 1600 lbs.
Total chest volume: 6000 lbs.
Day Three
Set 1: 200 x 12 = 2400 lbs.
Set 2: 200 x 10 = 2000 lbs.
Set 3: 200 x 8 = 1600 lbs.
Total chest volume: 6000 lbs.
Total weekly chest volume: 18,000 lbs.
In this example, that’s 4395 more pounds of volume for your chest and associated push muscles with the same number of sets per week!
And you know what? It’s more fun to do a few powerful sets of bench press or squats and be done. Less soreness, faster recovery, and less chance of injury. Count me in.
STUDIES
Effects of Resistance Training Frequency on Measures of Muscle Hypertrophy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs40279-016-0543-8
Resistance Training Frequencies of 3 and 6 Times Per Week Produce Similar Muscular Adaptations in Resistance-Trained Men
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30363041/
Effect of Resistance Training Frequency on Neuromuscular Performance and Muscle Morphology After 8 Weeks in Trained Men
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29528962/
Resistance Training with Single vs. Multi-joint Exercises at Equal Total Load Volume: Effects on Body Composition, Cardiorespiratory Fitness, and Muscle Strength
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29312007/
Effects of Consecutive Versus Non-consecutive Days of Resistance Training on Strength, Body Composition, and Red Blood Cells
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29967584/
Short-term effects of resistance training frequency on body composition and strength in middle-aged women
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21881534/
The effects of exercise variation in muscle thickness, maximal strength and motivation in resistance-trained men
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31881066/
Influence of High- and Low-Frequency Resistance Training on Lean Body Mass and Muscle Strength Gains in Untrained Men
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31009427/
Nonconsecutive versus consecutive-day resistance training in recreationally trained subjects
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27682004/
Evidence-Based Resistance Training Recommendations
Higher Training Frequency Is Important for Gaining Muscular Strength Under Volume-Matched Training
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30013480/
How many times per week should a muscle be trained to maximize muscle hypertrophy? A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies examining the effects of resistance training frequency
THE MOST POWERFUL INGREDIENT OF BLACK BOX VR
Our workout program is wrapped up in a virtual sport/game with the primary goal of increasing workout adherence over the long term (which is the ONLY secret to fitness success). Video games and sports are powerfully addictive! Very few people stick to their exercise programs. Very few people are consistent with their workouts. It turns out that almost nobody is consistent over the long-term. We are solving that problem using the most up-to-date game and social psychology.
Beneficial side effects of using a game are lower pain perception, faster time perception in a flow state, more player motivation to push hard because you are trying to win, and it’s way more fun and interesting than three sets of ten, repeat, repeat, repeat.
Instead of a personal trainer telling you to do a set of overhead presses, the game gives you autonomy to make your own choices… but the sport rules and mechanics are balanced so that, on average, you make the choices that we want you to. Games are smart like that.

This is not some side activity like pickleball. It’s your TRANSFORMATION machine and a whole new way to workout intensely and efficiently!
Variety reduces monotony and increases adherence. We want you to do a balanced, full-body workout and we want you to go to (or close to) muscular failure with each set, pushing yourself to a limit where your body will be forced to change, and we want you to do it safely and efficiently.
Black Box VR is a revolutionary new way to get super fit in record time! Our easy story-based onboarding makes it easy to learn no matter how new you are to games or exercise.
And you know what else is cool? Black Box VR is currently being studied by the UCLA UC Fit Lab. We’ve completed four university studies with more coming soon. Check our other posts for published results!




